Prenatal Genetics
The purpose of prenatal genetic testing is to provide information about the fetus's genetic status early in pregnancy and to screen for the risk of serious chromosomal abnormalities. One of the most modern, non-invasive tests in this field is the NIPT test.
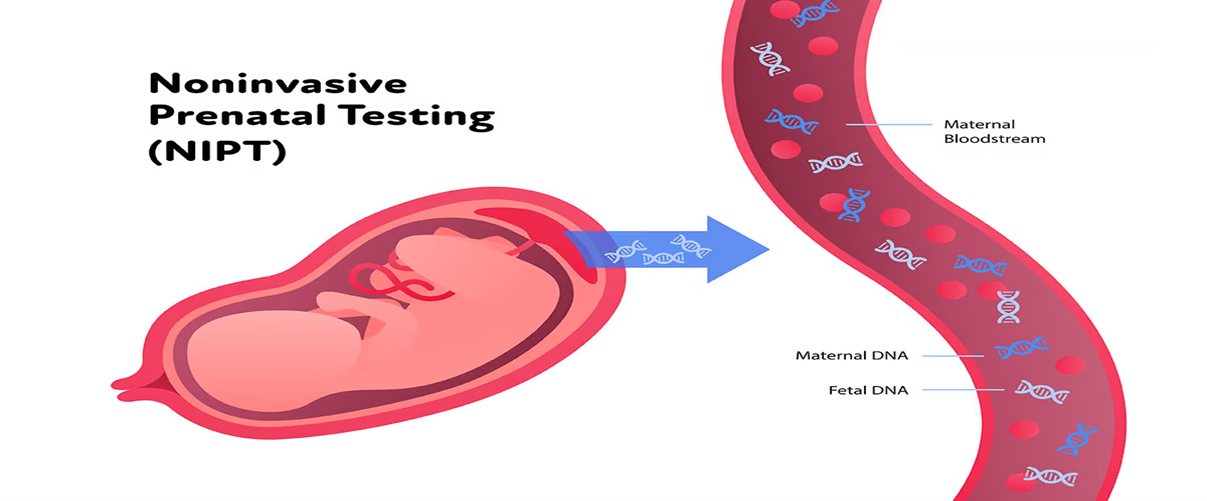
What is the NIPT Test?
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing
NIPT (Non-Invasive Prenatal Test) is a genetic screening test performed from maternal blood that analyzes fetal DNA (called cell-free fetal DNA). The test examines whether there is a higher probability of chromosomal abnormalities being present.
Conditions Detected by NIPT
- Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
- Sex chromosome abnormalities (e.g., Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome)
- Package-dependent additional screenings available
- High sensitivity for major chromosomal disorders
When Can It Be Performed?
- Available from 10-11 weeks of pregnancy
- Simple maternal blood draw procedure
- Earlier testing not recommended
- Requires adequate fetal DNA ratio in blood
- No special preparation needed
- Results typically available within 1-2 weeks
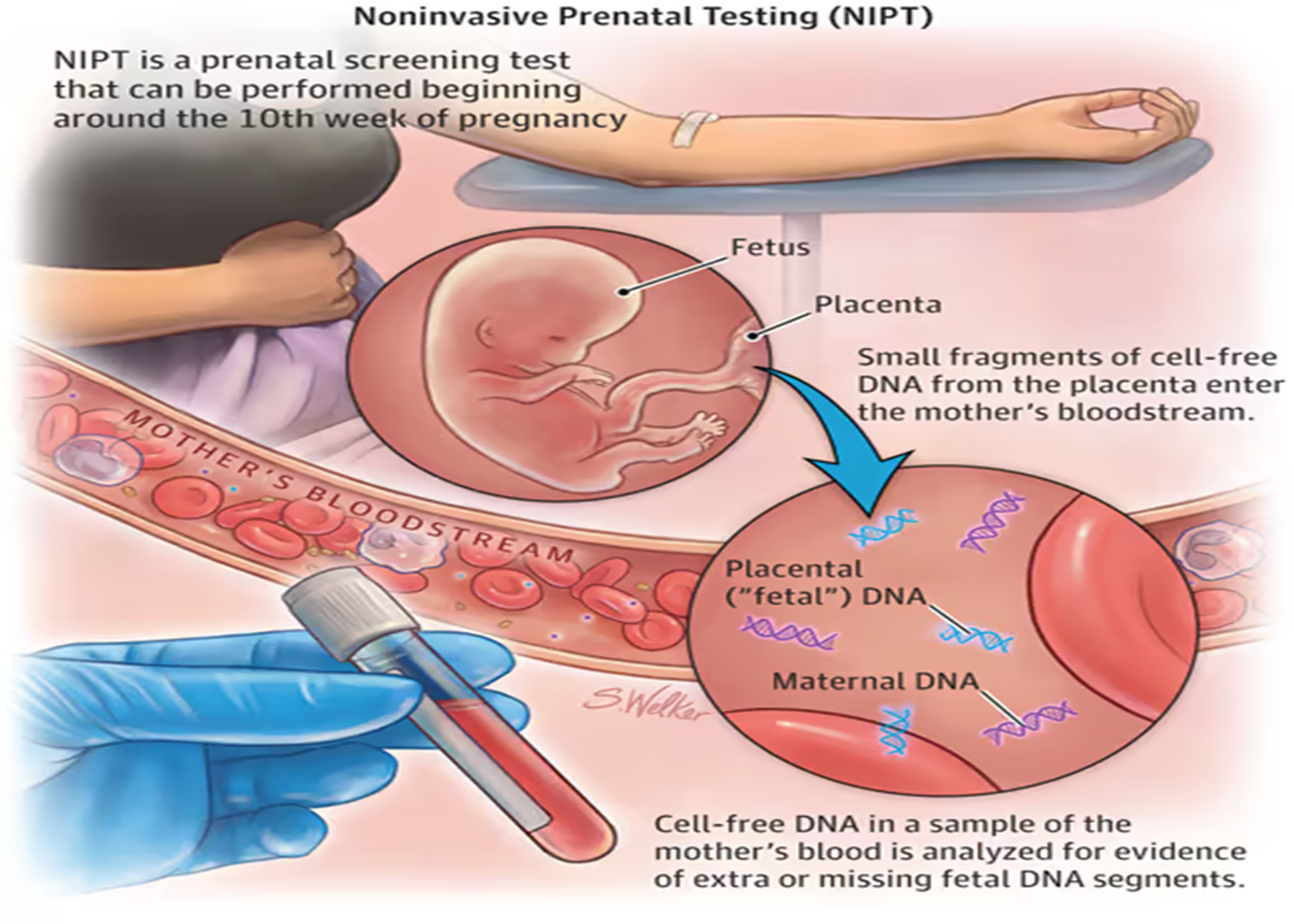
Important: Screening Test, Not Diagnosis
NIPT is not a diagnostic test, but rather a screening: it shows the probability that certain chromosomal abnormalities are present in the fetus.
What Happens if NIPT Shows an Abnormality?
If NIPT indicates a high risk for any chromosomal abnormality, then invasive diagnostic testing is recommended for confirmation. These procedures enable direct genetic testing of cells from the fetus or placenta.
Invasive Diagnostic Tests
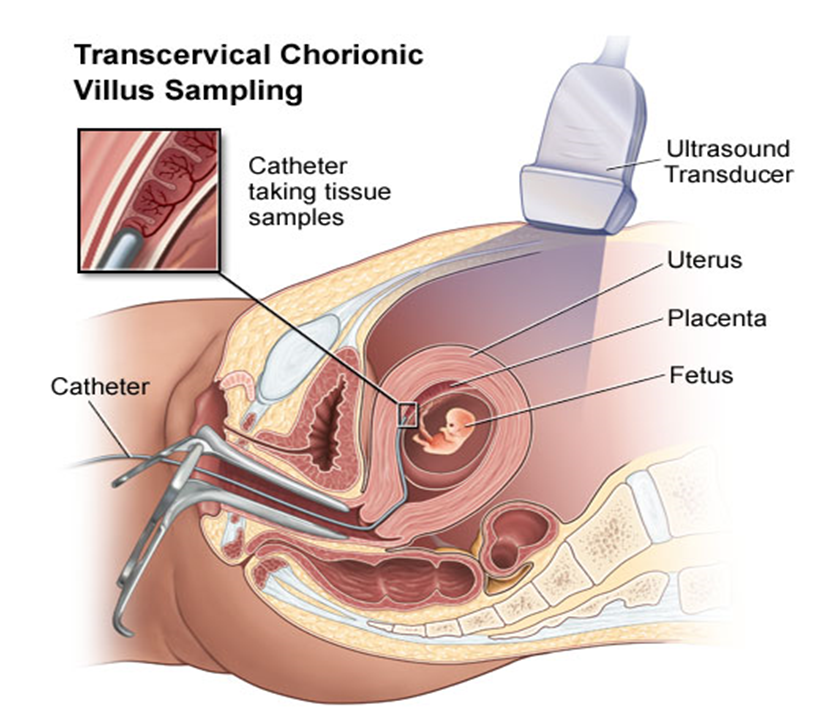
1. Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- Timing: Usually performed between 11-14 weeks
- Method: Sample taken from placenta
- Via vaginal or abdominal approach
- Performed under ultrasound guidance
- Purpose: Genetic diagnosis (chromosomal analysis or molecular testing)
- Small risk of miscarriage (0.1-0.5%)
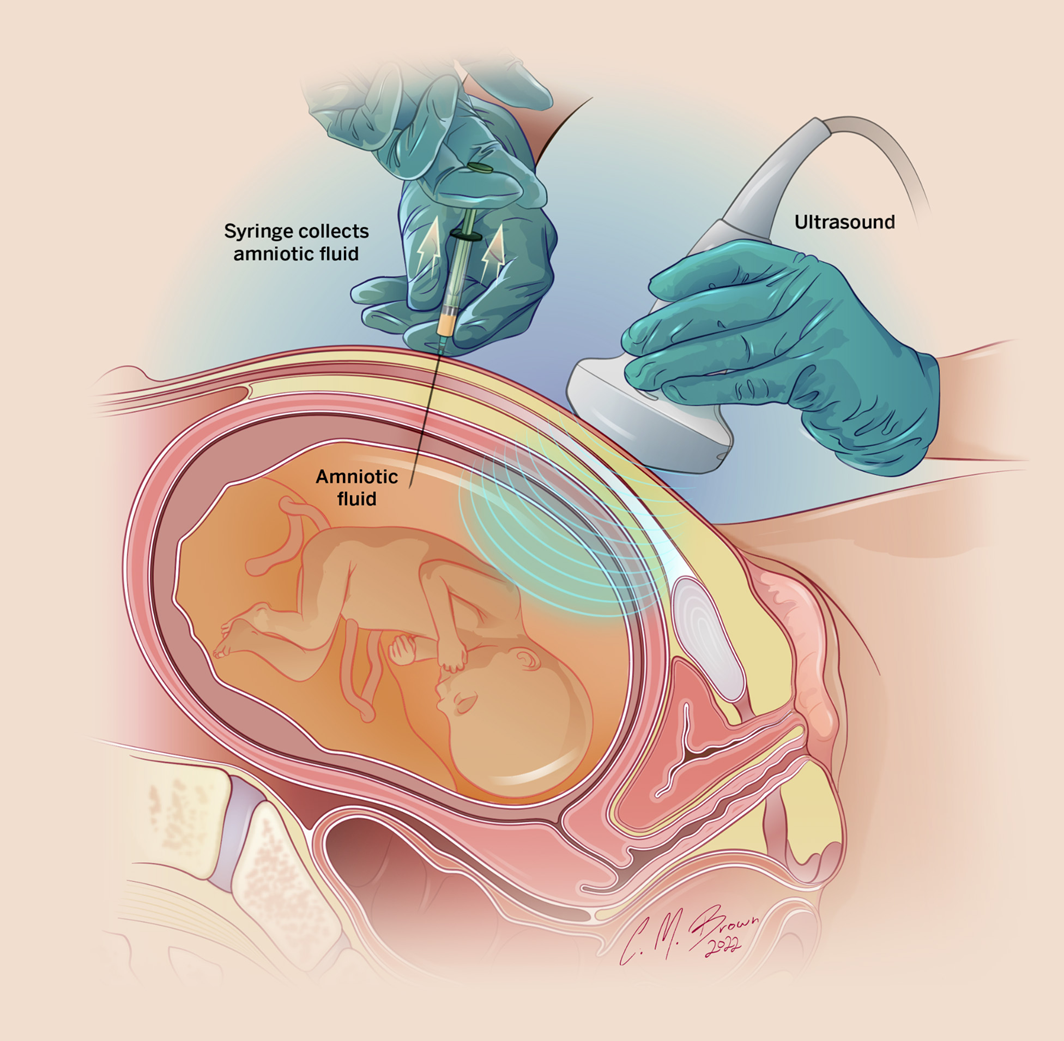
2. Amniocentesis
- Timing: Performed from 16 weeks onward
- Method: Thin needle through abdominal wall
- Amniotic fluid sample containing fetal cells
- Purpose: Chromosomal testing
- Additional genetic screening or infection detection
- Small risk of miscarriage (0.1-0.5%)
Important Risk Information
These tests provide accurate diagnosis, but may slightly increase the risk of miscarriage (0.1-0.5%).
Summary Comparison
| Test | When? | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIPT | 9-10 weeks onward | No miscarriage risk, high sensitivity | Not diagnostic |
| Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) | 11-14 weeks | Early diagnosis | Small miscarriage risk |
| Amniocentesis | From 16 weeks | Diagnosis, detailed testing | Small miscarriage risk, performed later |
Comprehensive Prenatal Genetic Testing
Our prenatal genetic testing services provide essential information for expectant parents, offering both non-invasive screening and confirmatory diagnostic options to ensure the best possible care throughout pregnancy.

